Robotics
Robotics is multidisciplinary research field involving topics including mechanical, control and electrical engineering as well as computer science and artificial intelligence. Robot technology is used when there is the requirement to carry out repetitive tasks, dangerous tasks, highly-precision tasks; health care and welfare tasks; etc.
A robot is an electro-mechanical machine that is programmed to perform specific tasks and it is usually composed by components such as mechanical, actuation, sensory and control systems. There are several environments where robot technology can be applied for example in the industry (e.g. solar cell panels assemble, steel bending, etc.), hazardous environments (e.g. nuclear plant monitoring and decommission, space exploration, etc.), in hospital environments (e.g. minimally-invasive brain surgery, medical staff training, etc.), home environment (e.g. assisting elderly and impaired people in their daily lives, etc.); etc. There are different reasons for using robot technology but the main reasons is to improve the efficiency and reduce costs of current production technologies, medical procedures, healthcare and welfare services, etc.
Even though the market size is still small at this moment, applied fields of intelligent systems (i.e. human friendly robots) are gradually spreading from the manufacturing industry to the others as one of the important components to support an aging society. The way a person interacts with human-friendly robots is quite different from interacting with the majority of industrial electro-mechanical systems today. The development of human-friendly robots drives research to develop autonomous and/or semi-autonomous systems that are natural and intuitive for the average consumer to interact with, communicate with, work with as partners, and teach new capabilities. In recent years, the benefits of designing robots based on biologically inspired principles have increasingly demonstrating novel advances in robot technology. Biologically inspired robotics is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach that aims to strengthen the collaboration between roboticists and biologists. Research in this field has successfully fused techniques from sensor fusion, artificial intelligence, neuroscience, simulation/modelling, and robotics. As a result, different applications have been proposed i.e. medical field.
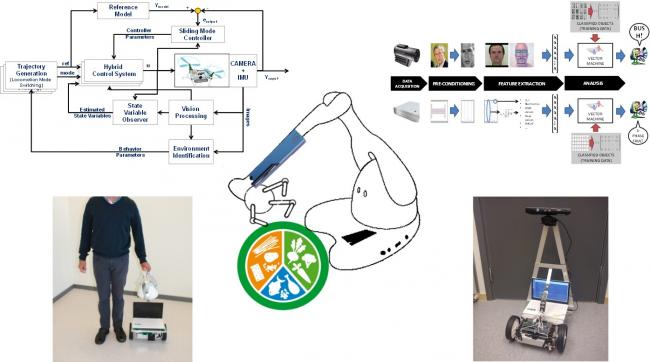
The current research carried out at the Department of Engineering and Physics is related to the development of haptic-based mobile robot with embodied bodily-kinaesthetic, perceptual and cognitive capabilities, the development of a biologically-inspired architecture for an intelligent robot vehicle with multimodal locomotion capabilities as well as the development of a human friendly robot vehicle. Other examples of projects currently pursued with researchers from other universities; such as Waseda University (Japan), SSSA-PERCRO (Italy), Warsaw University of Technology (Poland), Cassino University (Italy), etc. are humanoid robots, perceptual robots, educational robots, and medical robots.

